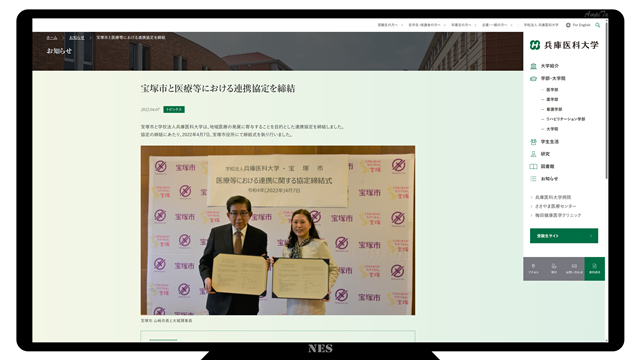
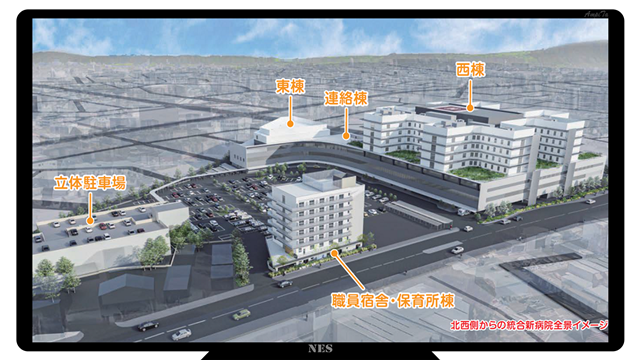
The Itami City Hospital and the Kinki Central Hospital of the Public School Mutual Aid Association will be merged and reborn as Itami City Itami General Medical Center (tentative name).
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
[Reference] Kinki Central Hospital: Reorganization of the integration between Kinki Central Hospital and Itami Hospital
[Reference] NES:Medical Survey Itami Hospital
Menu
- Locally rebuilt.
- High-priced local reconstruction
- The new hospital is a third-guessing emergency.
- A helicopter for 10km.
- Construction costs for rooftop heliport
- Limited emergency resources
- Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital and Doctor Car
- Emergency physician.
- Medical Department
- Heart-catching patient fight (?)
- From the ambulance to CT
- Disadvantageous logistics
- Hazard map
- Do you need a third emergency and disaster center hospital?
- Takarazuka City Hospital will be responsible for the tertiary emergency.
- 254billion yen donation
- Takarazuka City Hospital’s Itami Hospital
- The thoughts of the people of Takarazuka
- Discontinued Story
- Start with a blank sheet of paper.
- Ask the staff to open a business.
- Two hospitals by function
- The original draft of Nakanoshima (?)
- Complex hospitals by function
- Boosting the acute phase in the recovery phase
- Imaginary “recovery rehabilitation” hospital
- Number of beds (fantasy)
- Downsizing
- Regional Medical Cooperation Promotion Corporation
- The division of roles and livelihoods of regional medical care
- Rare medical services
- City 12Billion Yen + City Hospital 236Billion Yen
- If it is unprofitable in the public sector, it is a double suffering and triple suffering
- If the surplus continues, the management method of attention
- Medical fee revision under tight medical expenses
- What happens if the debt is not paid?
- You just have to do your best in managing the hospital.
- End of delusion.
Locally rebuilt.
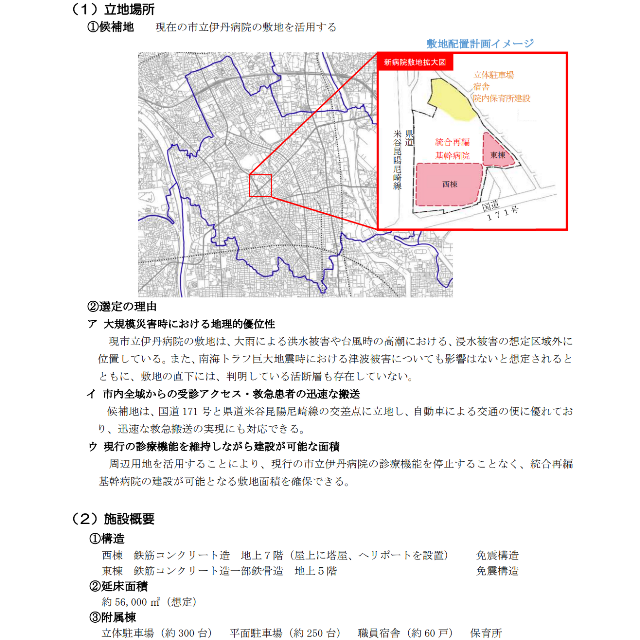
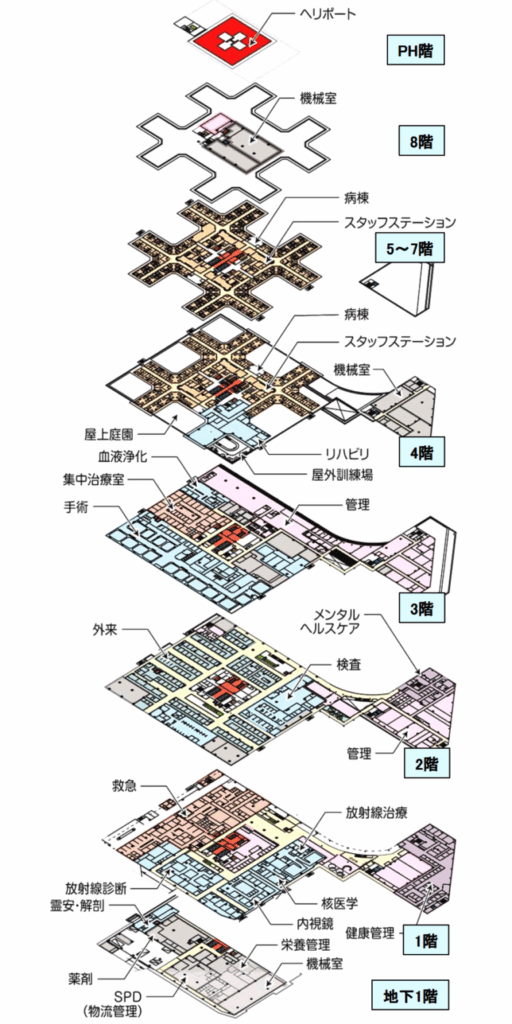
A new hospital will be built in the area of Itami Hospital. It is like a so-called local reconstruction, but since it is a merger of two hospitals, the size of the hospital bed will be large.
The new hospital is planned to have 602 floors, with 54 intensive care floors, 528 general hospital beds, and 20 palliative care beds.
The city’s Itami Hospital has 414 floors and Kinki Central Hospital has 445 floors. In short, we plan to build a 602-bed hospital in a space of 414 floors.
A video introducing the new hospital was released at the end of February 2025.
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
[Reference] Kinki Central Hospital: Reorganization of the integration between Kinki Central Hospital and Itami Hospital
[Reference] Providing safe and secure medical care trusted by the community and creating health–We have started the construction of a new integrated hospital –
[Reference] Itami Hospital Management Enhancement Plan for the City of Itami Hospital Overview Version
[Reference] Basic Policy on the Integrated Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
Mitsui Memorial Hospital, which was rebuilt over five years, has completed the “100th Anniversary Project Renovation Plan” under close planning.
The people involved said it was a very expensive job. From the foundation work, we do everything that can be done in one time and divide it into several times, so we also arrange heavy machinery etc. every time. The entry and exit of construction vehicles was limited, and expenses were only increasing.
Since it is a private hospital, there is no problem in cutting down on your own property, but local reconstruction at municipal hospitals is uneconomical if there is no suitable reason.
After the relocation of the city hall of Komoro Welfare Hospital in Nagano Prefecture, a hospital was built on the site of the former city hall. In addition to promoting rational construction by using the land in turn, the compact city concept was also realized.
In Itami City, both the city hall and the hospital have been rebuilt locally, and the place is 1.5km to 2km from the nearest station (Hankyu Itami Station). The municipal buses do not run on the entire line, the parking lot is not too much, it is not a place where the population is concentrated, and it is a place where the merits of local reconstruction are difficult to understand.
It is difficult to understand, I think that it is a local reconstruction because there are firmly merits, so I would like to investigate in the future.
[Reference] Mitsui Memorial Hospital 100th Anniversary
[Reference] Reconstruction of Komoro Welfare General Hospital
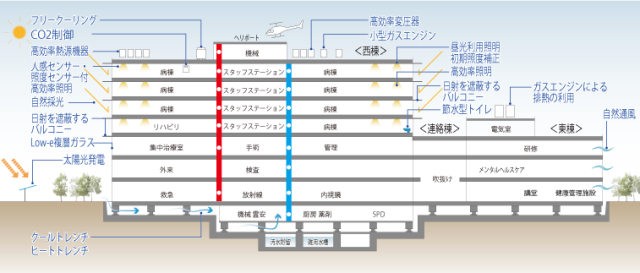
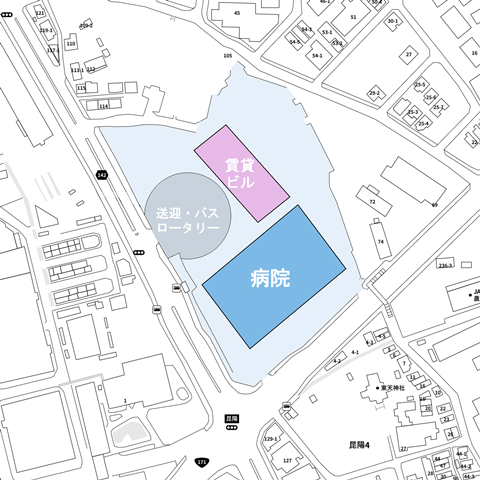
The new Itami hospital has a rooftop heliport, and there is a plan to be responsible for the tertiary emergency.
I think it is cool for those who say, “That was built by me”, but it seems that there is no clear data on whether tertiary emergency care is needed in this area.
If there is a tertiary emergency, patients will be transported, but just because there was no destination to carry the third patient, Hanshin Medical Area is not the case that there is no destination to carry the third patient.
If it is a private business, you should take risks, but since it is a municipal hospital, I hope that there is no bet on functions that do not know whether it is necessary or not.
[Reference] Third emergency (heavy)
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
[Reference] Kinki Central Hospital: Reorganization of the integration between Kinki Central Hospital and Itami Hospital
[Reference] Providing safe and secure medical care trusted by the community and creating health–We have started the construction of a new integrated hospital –
[Reference] Itami Hospital Management Enhancement Plan for the City of Itami Hospital Overview Version
[Reference] Basic Policy on the Integrated Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
If the municipal Itami Hospital announces the tertiary emergency, it may be the northernmost tertiary emergency hospital in the Hanshin medical area, and there may be a logic that a heliport is necessary because it becomes the northernmost point.
However, the helicopter is over 200km/hr, and it takes three minutes to Prefectural Amagasaki and Prefectural Nishinomiya beyond the Itami Hospital.
In fact, it takes off and heads to the hospital in a straight line, so the difference may not take less than three minutes.
The rooftop heliport has already been listed in the concept of a new hospital of the prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital, and the other side will open two years early, so I think that the Hanshin Medical Area can be left to the prefectural two hospitals.
[Reference] Third emergency (heavy)
In the new hospital concept, there is a rooftop heliport as a good-looking function called “cool”.
If I’m a general contractor salesperson, I might bring an exciting video and say, ‘Let’s build a heliport on the roof.’
If the municipal Itami Hospital announces the tertiary emergency, it may be the northernmost tertiary emergency hospital in the Hanshin medical area, and there may be a logic that a heliport is necessary because it becomes the northernmost point.
The rooftop heliport has already been listed in the concept of a new hospital of the prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital, and the other side will open two years early, so I think that the Hanshin Medical Area can be left to the prefectural two hospitals.
As for the position of the construction side, one house is a work, and the higher the function and cost, the more achievements it can be.
If the rooftop is only equipment such as air conditioner outdoor units and generators, it is only necessary to calculate the load capacity from its weight and strengthen the frame, but when it comes to a heliport, it is not possible to calculate simply by weight.
When landing, acceleration is taken into account in addition to the weight of the aircraft. Calculating the impact load involves a variety of complex factors.
When taking off, buoyancy is made with a propeller.
There is also friction caused by the contact of the helicopter on the roof. You will also need waterproofing that you expect it.
Since it is a premise to transport patients, it is designed so that a stretcher-compatible elevator goes to the rooftop. I don’t use it often, but it costs a lot of money for a floor.
Since it is a rooftop on the top of the 8th floor, if the pillars from 1 to 8 floors are thick for the heliport, it will be a considerable construction cost.
Maintenance costs such as elevators and waterproofing treatment can be endless.
Generators and outdoor units that should have been placed on the rooftop will be placed elsewhere, so the floor area will be extra.
In other hospitals, I think there were examples where the rooftop of the multi-story parking lot was a heliport.
At my previous job, a helicopter came to a nearby playground.
I think that the cancellation of the rooftop heliport is also a decision if the construction cost can be cut.
In order to take the third emergency, you will need people and things.
You can buy things such as CT and doctor cars, but people can not easily procure things.
If the number of emergency doctors is at the last of the three hospitals that are responsible for the tertiary emergency, the fight for doctors may begin by creating a fourth hospital. If you fight, you will be treated better by doctors, so that may be a good thing.
On the other hand, when it comes to competition between patients, there are concerns about the deterioration of the quality of medical care.
If the number of difficult cases is reduced, the number of experiences of doctors and nurses will decrease. Since the medical treatment is around the clock, you may work shifts, and if you do not hit it well, the blank may be long.
[Reference] Three times outside the Hanshin medical area
Even if you do not respond to tertiary emergency, there is a doctor car at Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital.
If you go to the patient parking lot of the hospital, you can see the vehicle located near it at any time.
The hospital has a well-developed medical treatment system, with more than 5,500 patients a year receiving ambulances and more than 3,500 hospitalizations. Accepting this number of hospitalizations means that there is a good connection between the emergency department and other departments.
Even in secondary emergency situations, it is thought that sufficiently advanced medical care is provided, so patients who are sent to tertiary emergency care are considered to be quite serious.

[Reference] Kansai Dekai Hospital: Doctor Car
[Reference] Kansai Rosai Hospital: Emergency Department
Kinki Central Hospital has two full-time doctors, and Itami Hospital has one full-time doctor.
There are three hospitals in total.
The emergency department of Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital mentioned above is ten people in total. There are also doctors who are concurrent in other departments, such as the Severe Treatment Department, so when it comes to critical care departments, there are two people.
At the Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center, it seems that five patients are enrolled in the emergency intensive care department and eight pediatric emergency intensive care departments are enrolled.
[Reference] Transport by ambulance
[Reference] Kinki Central Hospital: Emergency Medicine (Kinchu ER)
[Reference] City Itami Hospital:Emergency Medicine
[Reference] Kansai Deafness Hospital: Critical Care Medicine
[Reference] Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center: Emergency Intensive Care Department
[Reference] Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center: Department of Childhood Emergency Intensive Care
The current departments of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital are as follows.
Just because it is advocating, there is no assurance that there is a full-time doctor, nor is it actively accepting emergency care and surgery.
If you look closely on the website of Itami Hospital, there are eight doctors in the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine. On top of that, we are looking for a cardiologist. It is also certified as a training facility of the Japanese Society of Cardiovascular Medicine.
Not a single doctor is listed in the hospital’s cardiovascular surgery. There is also no information on the treatment results in other departments.
Cardiovascular surgeons are published on the website when they are certified. There seems to be no specialist belonging to the municipal Itami Hospital in that list, so there may not be a full-time specialist at present.
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Outline of the hospital
[Reference] Kinki Central Hospital: Overview of the hospital
[Reference] 3 Society of Society Organization Accreditation Organization of Cardiovascular Surgery Specialists: List of Cardiovascular and Vascular Surgery Specialists
In the Hanshin Medical Area, which has a population of 175 million, cardiac catheterization is performed 4,178 times a year.
It can be calculated as one case for every 420 people, but if you divide it by 365 days, there are only 11.45 cases per day. Even in 200 days, it’s 20.89 cases. This number will be shared with Hyogo Medical University and Amagasaki Medical Center.
The elderly population will increase for the time being, so the number of patients is expected to increase, but on the other hand, medical expenses will be tight, so the medical fee for the mentality is likely to become more severe.
The heart is not established by the doctor alone. Nurses, radiologists, and clinical engineers are involved in the categorization, and patients after categorization are sent to the ward and intensive care unit.
If the occupancy rate of the heart is lowered, it will be unprofitable, but it will be unprofitable even if the unit price falls too much.
If we cannot maintain the Angio equipment and human resources, we will not be able to stop withdrawing, so I think it will be necessary to adjust the resources in the region.
The number one cause of death in Japan is cancer (malignant neoplasms) and the second is heart disease. It was also a long time ago that cerebrovascular diseases ranked third, but now it is in fourth place because it has handed over the top to pneumonia and old age.
It is true that old age increased with the extension of healthy life expectancy and the increase in the number of elderly people, but it also contributes greatly that cerebrovascular disease has become a disease that can be saved.
In acute cerebrovascular diseases, first of all, the appearance of emergency services is important.
I was also at the hospital where I was working, but for patients who had been transported for suspected stroke, the emergency team also checked the diagnosis results and studied as long as time allowed.
You will learn not only how it is a hit, but how it looks like success / failure.
What is important here is to keep the CT room free from the request of the emergency team to the time of arrival of the ambulance.
They will be transported as soon as five minutes, or at least fifteen minutes later.
If you can move to the CT room as it is while wearing a monitor etc. after the ambulance arrives, the loss time in the hospital is zero, leading to the life of patients with cerebrovascular disease who are fighting for a moment.
If there is a possibility of applying tPA due to suspected cerebral infarction, the setup to insert the sheath into the groin area will also be parallel. After diagnosis, immediately start tPA amque, which increases the life-saving rate.
This system seems to have been established under the supervision of Mr. Toyoda, Director of Kansai Workers’ Compensation Hospital. If you know that the life-saving rate is high, I think that the emergency team will actively request the acceptance of Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital, so I feel that there is a synergistic effect.
The key is whether this system can be created at the new Itami hospital.
From our company, it is 4km to Kansai Labor Accident Hospital, and if you turn one signal, it is a straight line on the road with two lanes on one side to the hospital. The Itami Hospital is about 2.5km, but it needs to be bent three or four times. I think that if you get in an ambulance, you will be transported in a time that is not much different, so if you do not have a cerebrovascular disease emergency system at the new hospital, you will be transported to Kansai Labor Accident Hospital.
I want it to be a hospital of choice for emergency services.

[Reference] Cerebral intravascular treatment
As mentioned above, the existing four hospitals (Nishinomiya opened in 2026) have excellent access to highways and national roads.
The Itami Hospital faces the 171st National Route, but it is far from the expressway.
The Amagasaki Interchange on the Meishin Expressway is about 5km from the Ikeda Interchange and Takarazuka Interchange on the Chugoku Expressway, and the Amagasaki Interchange on the Meishin Expressway is about 5.5km away.
Takarazuka Interchange is the Takarazuka City Hospital, and the Amagasaki Interchange is the Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center, so it is not necessary.
The Hanshin Expressway is carried out by Hyogo Medical University and the Prefectural Nishinomiya General Medical Center, so this is also not necessary.
Since it is not an isolated disaster base hospital, somewhere DMAT will aim for the municipal Itami Hospital, but I think it is necessary to consider whether it is a reasonable thing.
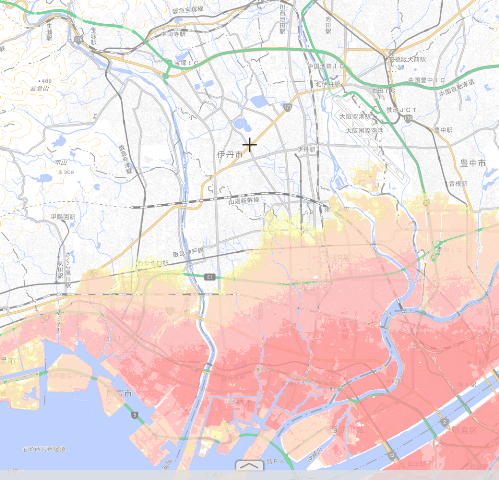
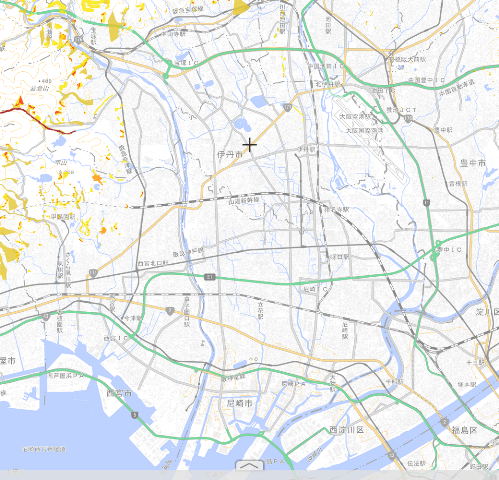
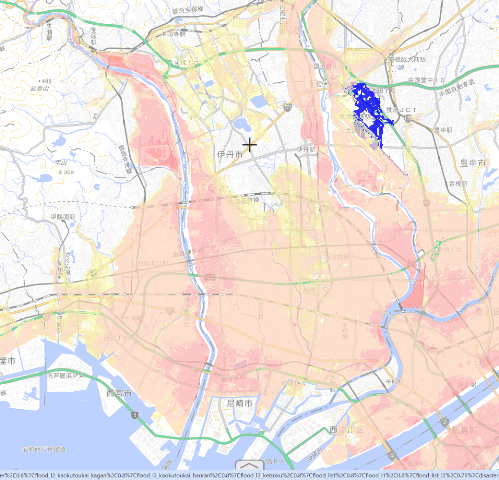
If you look at the hazard map of this area, it looks like the following.
The impact of the tsunami is likely to be at Hyogo Medical University, but other disaster base hospitals are expected to be able to escape the disaster. The Hanshin Expressway is elevated, so I think you can probably pass through, but the entrance and exit will be closed.
High tides are likely to have a very wide range of impacts. Disaster-based hospitals other than Takarazuka City Hospital are likely to have some impact.
If the high tide is temporary, the impact may be minor, but if the flooded road is not restored, it may not be able to function as a disaster base hospital.
There seems to be no risk to landslides. Even if the Chugoku Expressway is cut off, if you can use the Hanshin Expressway and the National Route2, it seems that you can secure a certain amount of rosy.
The flooding is likely to have some impact on the four hospitals of the disaster base hospital. The flooding of the Muko River and the Inona River is likely to affect the result.
If you look at the hazard map, the area around the municipal Itami Hospital may be intact. However, since the north, south, east-west roads may be cut off, so if there is no ambulance traffic, the value of the base will decrease.
It may be smoother to cross the border and get Osaka University Hospital as a DMAT base.
The Itami Hospital in the city is a good location as a function of some kind of disaster, but from the hazard map, it was expected that it would not be “one-of-a-kind”.
High tides are flooded by water rushing at once, but it is also a disaster that can be prepared to some extent, so the number of injured may not be so large.
This hazard map alone does not find a reason why ita is a disaster base hospital in the city.
As mentioned above, other disaster-based hospitals will respond, so I don’t think there is any reason to create a disaster-based hospital.
I think that it is just an explanation that it is not built in a bad place as a disaster base hospital.
When I say, “I am a tertiary emergency and disaster base,” there is something special, and it seems to be good for recruitment.
The sound of words alone does not generate money.
Construction is underway at Itami Hospital in the city with a project cost of one and a half billion yen for design supervision, one and a half billion yen for building relocation compensation, construction costs of 462billion yen, medical equipment, etc., and a total of 562billion yen for projects.
Itami City plans to bear 12billion yen, while it will bear 236billion yen by Itami Hospital.
In addition to spending so much on the project, it seems that it is difficult to do a surplus management by paying the cost of maintaining a disaster base hospital.
The new hospital seems to have a plan that will inevitably be in the black. I don’t know the details, but I think I’ll borrow it based on it and pay it back in the black part.
The story is whether it is necessary for the municipal Itami Hospital to take charge of the tertiary emergency and disaster base hospital.
Both of them are difficult to secure human resources, and I do not know how to maintain the human resources that I was able to secure because I have not inquired. There are no such articles on the Internet.
It has functions as a disaster base hospital, and strives to strengthen facility functions, such as strengthening earthquake resistance, maintaining and securing lifelines, securing helipads, securing and stockpiling medical equipment, stockpiling, and formulating BCP (business continuity plan).
In order to be able to conduct prompt and efficient relief activities in the early stages of the disaster, we will disseminate and raise awareness of knowledge of healthcare professionals, and develop a specializedly trained DMAT (Disaster Dispatch Medical Team) with the flexibility to be able to work in the acute phase of the disaster.
About the new core hospital
The hospital’s website says the above. It explains the function of the disaster base hospital, not the reason why it is a disaster base hospital.
[Reference] Third emergency (heavy)
[Reference] Disaster base hospital
[Reference] Providing safe and secure medical care trusted by the community and creating health–We have started the construction of a new integrated hospital –
[Reference] Itami Hospital Management Enhancement Plan for the City of Itami Hospital Overview Version
[Reference] Basic Policy on the Integrated Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
[Reference] Efforts for the establishment of a new hospital
[Reference] Takarazuka City: Determination of the new hospital construction site
[Reference] Takarazuka City Hospital aims for the image of the hospital (Takarazuka City, Takarazuka City Hospital)
For now, it is not known whether the new hospital of Takarazuka City Hospital will be responsible for the tertiary emergency.
Takarazuka City has concluded an agreement with Hyogo Medical University, which includes matters related to tertiary emergency patients.
Geographically speaking, for residents in the northwestern part of the Hanshin Medical Area, if Takarazuka City Hospital is responsible for the tertiary emergency, it is possible to shorten the time from 10km to go from Takarazuka Interchange to Hyogo Medical University and Prefectural Nishinomiya, so I think it is a dramatic improvement.
When starting from Shin-Mita Station, it is 38km to Hyogo Medical University, and from Kobe’s three major ICs to Takarazuka ICs, it is about 20minutes because it is a highway, but since it is a general road from Takarazuka IC, the distance is short but it seems to take about 20minutes. I think that there is not much time difference between going to Kobe University and Kobe Nichishin.
[Reference] Trends of Takarazuka City Hospital
[Reference] Hyogo Medical University: Takarazuka City and Medical Association Signed a Partnership Agreement with Takarazuka City
[Reference] Takarazuka City: Takarazuka City Hospital Management Enhancement Plan Overview Edition Reiwa 6th March
[Reference] Takarazuka City: Takarazuka City Hospital aims for the image of the hospital
[Reference] Takarazuka City: Takarazuka City Hospital aims for the image of the hospital that Takarazuka City Hospital aims for Overview version
[Reference] Takarazuka City: Guidelines for Strengthening Public Hospital Management to Ensure a System for Sustainable Regional Medical Care
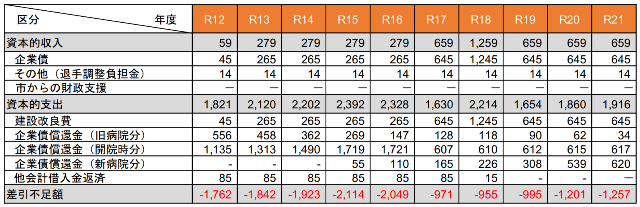
The ordinary profit and loss of Takarazuka City Hospital is in the black of 388,562 million yen in the 5th fiscal year of Reiwa, and in the fourth fiscal year of Reiwa, the surplus of 588,697 million yen. The surplus of undistributed profit at the end of the 5th fiscal year of Reiwa is 17billion yen.
The hospital’s reconstruction plan is in the process of concretely progressing, but the size of the hospital bed has been downsized to 350beds, and the estimated project cost is estimated to be 397billion yen.
A donation of £250m was made there. Since the reconstruction cost (excluding demolition costs) is 25183million yen, I think that I may have donated by looking at this figure.

Takarazuka City seems to have planned to raise funds by issuing public corporate bonds, and if corporate bonds were issued, the interest rate would have been several hundred million yen per year.
The donation is two and a half billion yen, but considering the interest rate, I think it has an economic value of about three billion yen.
Since the proceeds from the donation are the proceeds from the procurement of surgical support robots, it is like the introduction of an surgical support robot to the hospital.
As hospitals become more sophisticated, if they are able to avoid debt repayments and interest payments through borrowing, the amount that can be used for the next investment increases from the annual surplus amount to the next investment increases.
[Reference] Nikkei: The couple of Hyogo and Takarazuka donated 254billion yen to the construction of the municipal hospital, etc.
[Reference] NHK: Donation of approximately 25Billion yen from citizens, funds for rebuilding municipal hospitals, etc. Hyogo Takarazuka
[Reference] Takarazuka City
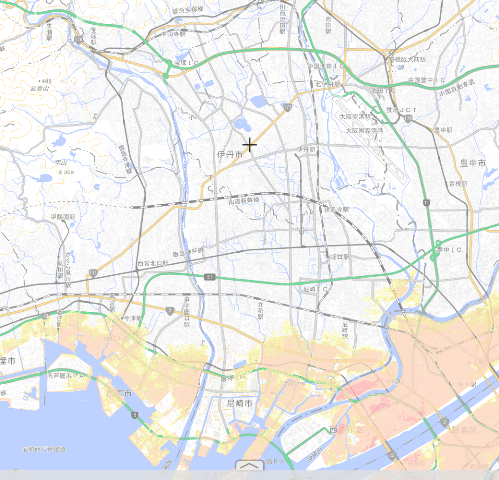
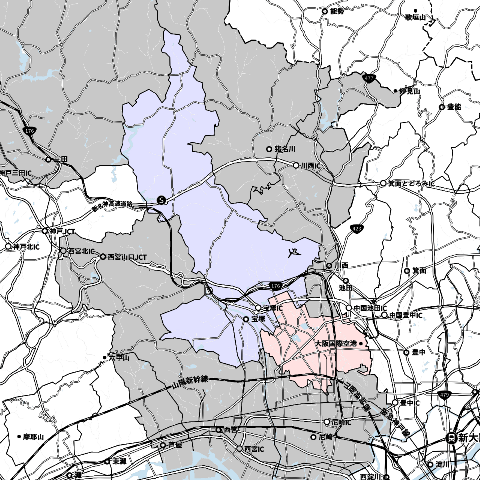
The location relationship between Takarazuka City and Itami City is as shown in the figure below. From Itami City, about one-fifth of the outer circumference is in contact with Takarazuka City.
Takarazuka has a population of 22 million, an area of 102sq km and a population density of 2,166 people/sq km.
Itami has a population of 200,000, an area of 25sq km and a population density of 7,791 people/sq km.
Both cities are operated by JR and Hankyu.
JR is a line that can travel between JR Takarazuka Station and JR Itami Station on the JR Takarazuka Line northward from Amagasaki, and it is a line that can be accessed between two cities.
There is no direct line between Takarazuka City and Itami City, and Hankyu Takarazuka Station, where the Takarazuka Grand Theater is located, is the starting point of the Hankyu Takarazuka Line, which runs directly from Osaka Umeda Station. It runs side by side with JR to Kawanishi, but after that it is a route through Ikeda City and Toyonaka City.
Takarazuka Station is also the first station on the Imazu Line. It goes south and goes back and forth between Nishinomiya Kitaguchi Station.
The Hankyu Itami Line is a short line that runs between Hankyu Itami Station and Hankyu Tsukaguchi Station. You can transfer to the Kobe Line from Tsukaguchi to go to Umeda or Sannomiya, but if you want to go to Hankyu Takarazuka Station from Hankyu Itami Station, you need to transfer twice.
JR and Hankyu do not have a mutual transfer, so it is a transfer outside the ticket gate. Takarazuka Station is adjacent, but because it is far away, it is not an image of transfer outside the ticket gate, but it is a completely different station.
If you think about it by car, I think that Takarazuka and Itami are very close.
AEON Mall Itami Konyo, which is close to the city border, is also attracting cars from the Itami area and Takarazuka.
Because the north-south roads are developed, not only the Amago Line where the Takarazuka Inter is located, but also the north-south road that passes through place names such as Yasukura, Aramaki, and Yamamoto has a lot of traffic.
If the medical functions of Takarazuka City Hospital are fully equipped, the question of whether it will be an easy place for Itami citizens to go to is probably deeply related to the business plan of Takarazuka City Hospital.
For people who use a car, I think that there is not much difference in the time required from the case of going to Prefectural Amagasaki or Kansai Labor Accident. Especially for Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital, it is located along the same Amaho Line, so I think there are many Itami citizens who go north after going to the Amaho Line or go south.
For those who frequently use National Route 176, I think it is more familiar to go to Takarazuka than to go to Amagasaki on the south side.
At present, the citizens of Itami who attend Takarazuka City Hospital are limited, and I think that Takarazuka citizens who go to the municipal Itami Hospital are also limited.
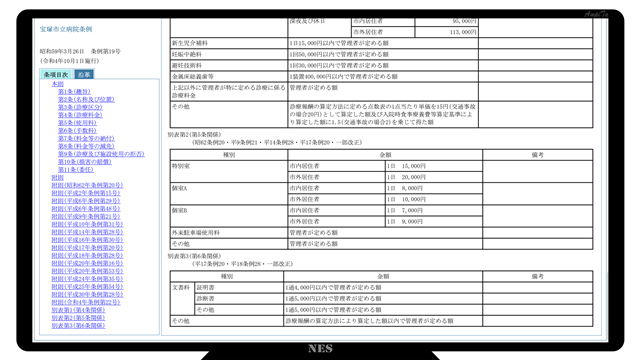
At the time of hospitalization, there is a system that citizens are discounted about the private room fee. Takarazuka City Hospital offers a discount of 2,000yen for private rooms and 5,000yen for special rooms. The Itami Hospital has a discount of 3,300yen for private rooms and 5,500yen for special room A.
When considering using a private room, it is more economical for citizens to be admitted to the local municipal hospital.
If the functions of the hospital are clearly different, I think that there is a possibility that it will be selectively aimed at either.
If Takarazuka City Hospital becomes more sophisticated in several departments, it is possible that the number of patients who want to become Takarazuka City Hospital even if it is not medically advanced, if it is said that it has become more sophisticated by review, even if it is a citizen of Itami City, there is a possibility that the number of patients who are aiming for Takarazuka City Hospital will increase.
As a university hospital, even if it is a famous hospital to some extent, the treatment area is about 10km, and in the area where there are few medical institutions, it is about 20km. I don’t have the base data with me.
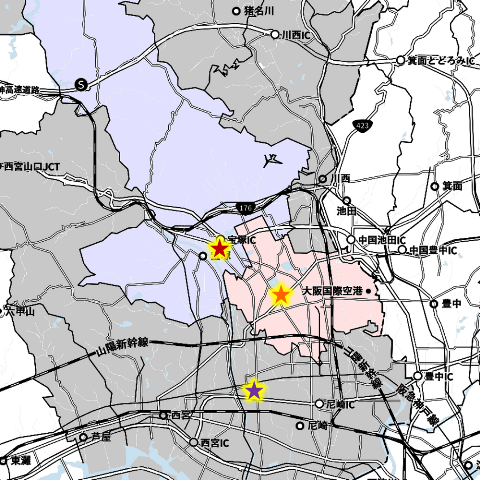
The red circle in the figure below has a radius of 5km and a blue circle has a radius of 10km. Roughly speaking, I think that there are close to three hundred thousand people living in the 5km area and eighty thousand people in the 10km range.
The only hospital with more than 200beds of general hospital beds within 5km is the Municipal Itami Hospital.
In the 10km area, Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital and Prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital will enter. Hyogo Medical University and Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center are also within 10km of the last minute.
In other words, if you look at the 10km area, there are many competitors, but if you are in the 5km area, there are few competing medical institutions.
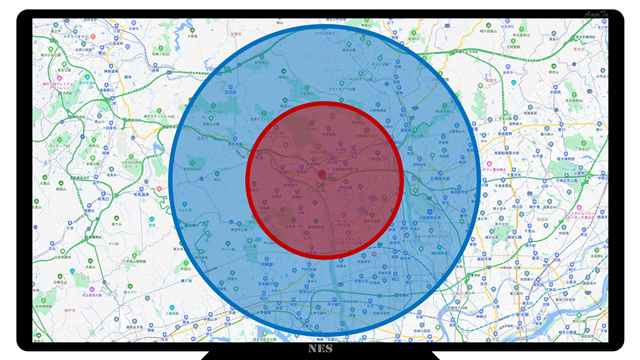
In terms of business strategy, Takarazuka City Hospital is thought to be able to secure the number of patients even if the population declines and enters the era of population decline, if the number of patients in the city Itami Hospital is in inflow.
Medical care is also a business, so management will be stable if you perform medical care with high profit margins and low-risk medical care.
For example, if laparoscopic surgery in the gastroenterology surgery and robot-assisted surgery can be performed a thousand times a year, the operation of related gastroenterology endoscopy and CT examinations will be increased together, and management will be successful.
If the current situation is six hundred cases a year, and a thousand cases that are not available at all as they are now, if the number is enough to be delivered if it is inflow from the area of another hospital, it may be natural for management to aim there. Whether it’s humane or not, it’s a different story.
Currently, Takarazuka City Hospital does not have a slogan of gastroenterological surgery.
[Reference] Takarazuka City Hospital Ordinance
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Inpatient Information, 6. Pay for hospitalization fees
To get to Hyogoshina University from Takarazuka Station, JR Takarazuka – JR Osaka – Hanshin Osaka Umeda – Mukogawa route, or the route from Hankyu Takarazuka – Nishinomiya Kitaguchi – Imazu – Mukogawa, all require transfer, and the time required is around an hour.
If you are a private car, you can reach most of it in about 15km south along the Amaho Line or Muko River, and if it is good, you can arrive in about 40minutes. A taxi costs about six thousand yen. It is about half an hour at Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital, and about five thousand yen by taxi.
When I was introduced to a large hospital and went to Amagasaki and Nishinomiya, it was a day job. Neither the patient nor the accompanying family member is easy.
If it is a rare disease or difficult surgery, you may give up, but if you are forced to be inconvenient due to lack of manpower or equipment, there may be parts that do not understand.
If the donation of two and a half billion yen was intended to be made with the intention of enhancing medical services to citizens, I believe that it will not end with the reconstruction of the building.
What was planned for downsizing from 350s to 380s may be 436beds to maintain the status quo, and even if the hospital bed is reduced, it may improve medical function.
Takarazuka Iso Hospital, the most recent in the city, has 160beds for sanatorium treatment, and Takarazuka Rehabilitation Hospital is a hospital with 162beds of convalescent rehabilitation beds.
Both hospitals are newly opened by a medical corporation that is already running a hospital, so I think that they are opening because they judged that there is a demand.
In both hospitals, basically the acute phase is not treated, and it is thought that it is a hospital that accepts patients in the recovery and chronic phase after finishing treatment at an acute stage hospital somewhere.
If the acute phase hospital in front of you becomes active, these two hospitals may also be active. In other words, it can be said that the expansion of the functions of Takarazuka City Hospital will affect other hospitals in the city.
| Hospital name | Number of hospital beds | Opened |
|---|---|---|
| Takarazuka City Hospital | 436Floor | May 1984 |
| Medical Corporation Showakai Takarazuka Daiichi Hospital | 199Floor | July 1967 (Omuro Hospital) |
| Medical Corporation Showakai Takarazuka Rehabilitation Hospital | 162Floor | April 2008 |
| Takarazuka Iso Hospital | 160Floor | August 2014 |
| Medical Corporation Aishinkai Totakarazuka Sato Hospital | 136Floor | June 2001 |
| Medical Corporation Reciprocation Association Takarazuka Hospital | 131st floor | March 1956 |
| Kodama Hospital | 110Floor | Category: 1970s (1948Kodama Hospital) |
Artificial joint replacement is a major surgery and the hospitalization period is two to three weeks. When the family takes care of and visits, I think that it is easy to go back and forth in the city.
Postoperative rehabilitation is long-term and a large-scale work for patients. If you can transfer to a hospital where cooperation with the hospital where the surgery is performed, it seems to be good for both the patient and the family.
If you can create such a flow of surgery at Takarazuka City Hospital, which you will be able to perform surgery at Takarazuka Rehabilitation Hospital, spend your recovery period at Takarazuka Rehabilitation Hospital (160th floor), and transfer to Takarazuka Iso Hospital (160th floor), I think that there will be few negative aspects for citizens.
The convalescent rehabilitation ward is deeply involved in orthopedics, neurosurgery, cardiovascular medicine, and cardiovascular surgery, so if these departments are enriched, the more severe the convalescent rehabilitation ward in Takarazuka City may be in short supply, but if there is a demand, there may be movements such as hospital bed conversion and new openings.
[Reference] Takarazuka Daiichi Hospital: History
[Reference] Showakai: Takarazuka Rehabilitation Hospital celebrates its 15th anniversary.
[Reference] Kakogawa Iso Hospital: Takarazuka Iso Hospital opened on August 1st.
[Reference] Totakarazuka Sato Hospital: History and Facility Standards
[Reference] Reciprocation Kai Takarazuka Hospital: Greetings from the Director
[Reference] Kodama Hospital: Director’s greetings
I am worried that the story of the municipal Itami Hospital was progressing on the story of rebuilding because it was aging.
I think that I simulated what the impact would be if I went out of business now, but I would like to know what the result was.
The Hanshin Medical Area has a large population, and there are many medical institutions because they are adjacent to Kobe and Osaka.
I don’t think there are any departments or diseases that can’t be treated if the Itami Hospital is gone.
I think there is an opinion that it will be inconvenient.
The Medical Practitioners Act requires a curfew, so if you are in the daytime on weekdays, you should be able to see a doctor if you go to a medical institution somewhere. It is not a medical district with a hospital with a radius of 4km.
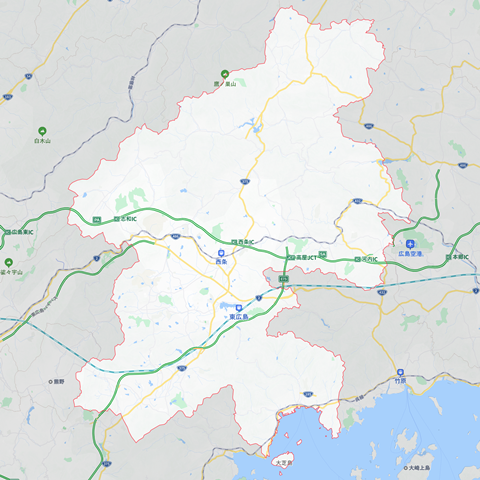
The Hiroshima Central Medical Area, to which Higashi-Hiroshima City is close to the population of Itami City, is 795sq km and 230K people, so the population density is greatly different.
The figure below is Higashi-Hiroshima City, but about half of the area of 635sq km, there is not a single hospital on the north side of the China Expressway.
If we are to reduce the number of hospitals from such areas, I think that the local residents will not be silent.
In Higashi-Hiroshima City, we are working hard to secure access to medical care by accepting the situation, attracting demonstration of autonomous driving, etc.
In the case of Itami City, there is also potential in the city. The top two hospitals are closed, but there are sixty-eight general hospital beds, including the bed clinic.
| Name | Total beds | General in bed | recuperation in bed | Psychiatry in bed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinki Central Hospital of the Public Schools Mutual Aid Association | 445 | 445 | 0 | 0 |
| Itami Hospital | 414 | 414 | 0 | 0 |
| Medical Corporation Mizukokai Itami Tenjingawa Hospital | 267 | 0 | 35 | 232 |
| Medical Corporation Seifukai Hanshin Rehabilitation Hospital | 192 | 192 | 0 | 0 |
| Medical corporation Seifukai Itami Seifu Hospital | 178 | 80 | 98 | 0 |
| Toyoakekai, Japan, Japan | 103 | 0 | 103 | 0 |
| Miyasou Hospital | 97 | 49 | 48 | 0 |
| Yusei Hospital, Yuseikai, Medical Corporation | 83 | 54 | 29 | 0 |
| Tsuneo Itami Neurosurgery Hospital | 80 | 80 | 0 | 0 |
| Medical Corporation Hoshishokai Aoi Hospital | 39 | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Yoshie Gastroenterology | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Medical Corporation Incorporated Association Hoshakukai Seiyu Clinic | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Medical Corporation Ryokushinkai Ohashi Clinic | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Shoji Surgeon | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Ota Surgical Clinic | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| 2nd Nishihara Clinic | 19 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Mizuho Ladies Clinic | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
If the municipal Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital go out of business at the same time, there will be employment problems.
Although it is temporary, there are many issues such as spending such as compensation money to increase, and having to go out of the city because there is no margin in the city for job hunting.
If it is a story of closure, there is no need to rebuild an old hospital, so the hospital can continue to operate until the last minute you can use it.
It may be possible to find a place to re-employ employees while adjusting the closing time.
Currently, it is the municipal Itami Hospital and Kinki Chuo Hospital, which are in charge of secondary emergency care and perform thousands of surgeries, but the past is left behind, and I will think about it with a blank sheet for the time being.
I think that by imagining the situation where two hospitals are now gone, and by thinking about what kind of hospitals will be needed and whether they are not needed at all, I think that the future of hospital management can be foreseen.
Major functions include outpatient care, hospitalization, emergency surgery, health check-up, and medical check-ups.
The focus of the outpatient clinic changes depending on whether there is an inpatient hospital bed or not. The same goes for emergency.
The focus of the hospitalization will also change depending on whether the surgery is possible or not. The same goes for emergency.
If so, you need to consider the operation.
If a total of seven to eight thousand surgeries are performed per year in both hospitals, this bearer will evaporate. If the weekday is 240days, the demand for surgery of about 30days a day will be free.
If you look at orthopedics, there are 1,583 cases in Itami Hospital and 126 cases in Kinki Chuo Hospital. The municipal Itami Hospital has opened an artificial joint center and performs about eight hundred artificial joint surgeries a year.
In order to perform such a large number of orthopedic surgeries, we should have been focusing on regional cooperation as a medical department, so it seems that we can create a concept of a hospital that makes use of this function as a whole.
Seven surgeries a day with 240days of operating the operating room a year, and from this figure, it seems that the management of one small hospital is possible.
Although it is not limited to orthopedics, the number of doctors in the rehabilitation department is five doctors concurrently in Itami City, and in the Kinki-Chuo region there are zero. The city of Itami has eleven physical therapists and four occupational therapists, and strengthening this is likely to be a challenge.
With regard to diseases related to respiratory and allergic diseases, the Department of Rheumatology for Allergic Diseases in Itami City has six doctors and ten patients with respiratory medicine.
If it is a small hospital, I think that it is also possible to establish internal medicine with a focus on respiratory medicine and allergies.
I think it is up to the doctor whether it is a strategy to choose to choose not to touch the circulatory system or to boldly enrich cardiovascular surgery and enhance cardiovascular medicine.
I feel that it is a good idea to give up to Kansai Industrial Accident Hospital for five people in both hospitals for neurosurgery.
The digestive system is a disease that is common in Japanese people, and there are many doctors, so if the system is in place, it is a good medical department. There are eight people in the gastroenterology surgery in the city and seventeen in the gastroenterology department. In the Kinki center, there are five people in the Department of Gastroenterology and seven members of the Surgery Department, and there are seven members of the surgery.
We will look at the medical departments where there is also a lot of demand for free medical care.
There are three dermatology in the city Itami and zero in Kinki-chuo. There are two people in Itami City and one in Kinki Chuo. There are five mammary surgeons in the city Itami, and there are no skeletal features in the central part of the Kinki region.
In this area, severe illness may be in cooperation with prefectural hospitals and university hospitals, and other than that, it may be good to cooperate with local practitioners.
There are three people in Itami City and three in Kinki Chuo. There are many clinics specializing in ophthalmology in the neighborhood, and the competition seems to be fierce because they are actively operating at other clinics.
In terms of childhood and perinatal period, it is home to nine pediatrics, one pediatric surgeon, and ten obstetrics and gynecologists at Itami Hospital. Kinki Central Hospital has two pediatricians and two obstetrics and gynecology.
The maternity and gynecologist’s office is closed one after another due to the elderly of the director, so it may be necessary to maintain the maternity department even if you receive a grant from the city.
As for pediatrics, the prefectural Amagasaki is full of them, so there is no need to overdo it, but there is also cooperation with obstetrics, and if you can get a grant from the city, I think it would be good to maintain it.
It seems that artificial dialysis is operated on ten floors at Itami Hospital, but this may be enough for hospitalization, but it is necessary to increase it to about ten times in order to generate revenue in an outpatient clinic.
It’s just the author’s fantasy. There is no basis.
In the previous section, I had a delusion on a zero-based basis that once I went out of business and opened a new business.
Actually, I think that it will be a continuation by shrinking the scale rather than completely closing down, but I will think about how to follow up on the medical departments that are revised and abolished due to reduction, including employment.
If the department that was divided by one or two doctors was profitable, why not have the new hospital open in front of the gate instead of advocating the same department?
By preparing a clinic mall like an outpatient center on the premises and renting it out as a medical department designation, if it is firmly buried, the medical treatment function can be maintained.
If home visits to the ward can be carried out to the extent that insurance allows, the quality of medical care may be maintained without declining even if the size of the hospital becomes small.
Since it is unavoidable to talk about it due to hospital convenience, when I stand on the position of a practitioner, I wonder if there is profitability by opening it in the current Itami Hospital location, and what is that location.
If you look at the surrounding population alone, it is not a favorable condition.
The south side is a two-lane national road on one side, so it is troublesome to cross, and there are many places other than houses such as shrines, agricultural cooperatives, elementary schools, etc., and many of the dwellings are detached houses. In other words, the population per unit area is small.
The west side is also a two-lane prefectural road on one side, and along the road is Sumitomo Electric’s factory for several hundred meters. The population of the location of the station is 3365m2, and I think that the apartment group can develop a capacity of 3,000units, but the population of the location is 528people, and the number of people over 65 is 45people.
If you go further west, you will find the Alvis Temple Book of the old public corporation, with a population of 1,251people and 455people over the age of 65. Since there are many clinics in the vicinity of Izumiya in the direction of the Amago Line, it is not easy to go to the Itami Hospital of the city because there are almost everything necessary for daily life such as banks.
Even if you go by car, if you can have a clinic mall in Izmiya, there are plenty of parking lots, cafes and fast food that kills time, so I feel that the side of the hospital where there is nothing lacks centripetal force.
[Reference] Sumitomo Electric: Itami Seisakusho
[Reference] Itami City: Population and number of households by age by town and aza (basic resident register, foreign registered population / five-year-old classification) Quarterly
The Hyogo Prefectural Disaster Medical Center and the Kobe Red Cross Hospital, which are also the main disaster base hospitals in Hyogo Prefecture, are located on the same site and have two hospitals in one building. The founders are Hyogo Prefecture and the Japanese Red Cross Society, a completely different organization.
The following three facilities are located in the same area. The two are located in the same building.
- Tokyo Metropolitan Hospital Organization, Tokyo Metropolitan Tama General Medical Center(789th floor)
- 2-8, 2-8, Musashidai, Fuchu-shi, Tokyo
- Tokyo Metropolitan Hospital Organization Tokyo Metropolitan Children’s General Medical Center(561st floor)
- 2-8, 2-8, Musashidai, Fuchu-shi, Tokyo
- Tokyo Metropolitan Fuchu Rehabilitation Center(260beds)
- 2nd and 9th Musashidai, Fuchu-shi, Tokyo
In terms of the complex, the international center for future medical care “Nakanoshima Qross” is a form that looks like a hospital moving in a large commercial facility.
Sakurabashi Watanabe Mirai Medical Hospital is located on the 7th to 11th floors, but there are member-only health check-up facilities, clinics, and pharmacies.
[Reference] Formation of Nakanoshima Qross, an international base for future medical care in Osaka Prefecture
by Nakanoshima Qross
About ten years ago, I came up with a plan for a redevelopment project in Osaka.
At that time, I had a relationship with the head of the medical school, so I was paranoid in that flow.
At that time, the number of inbound tourists exceeded thirty-six million, but at that time it was still at the stage of aiming for twenty-four million people. We were in the midst of a discussion about what would happen to the IR and casinos.
I had the opportunity to talk to the president of Marina Bay Sands in Singapore and asked, “Why Japan?” I dug the point deep.
Japanese food and festivals in Japan are popular with foreigners, but medical care is also attractive for high levels, so I drew up the concept of medical tourism.
It started with a picture like the figure below in terms of the first rough plan, realization on a low budget.

As the investigation progressed, it became clear that it was difficult for Osaka University Hospital, which is located in the Toyono Medical Area, to secure a hospital bed in the Nakanoshima area of the Osaka City Medical Area.
The concept of virtual ICUs came up from the question of how many floors can be secured. Many of the doctors’ resources remain at Osaka University, and some doctors and nurses are treated in Nakanoshima.
At that time, there was no zoom, and we used dedicated devices such as videophones and video conferencing systems, but if you call it “gathering”, about twenty departments will consider cases at the same time, and such things would be possible in the future.
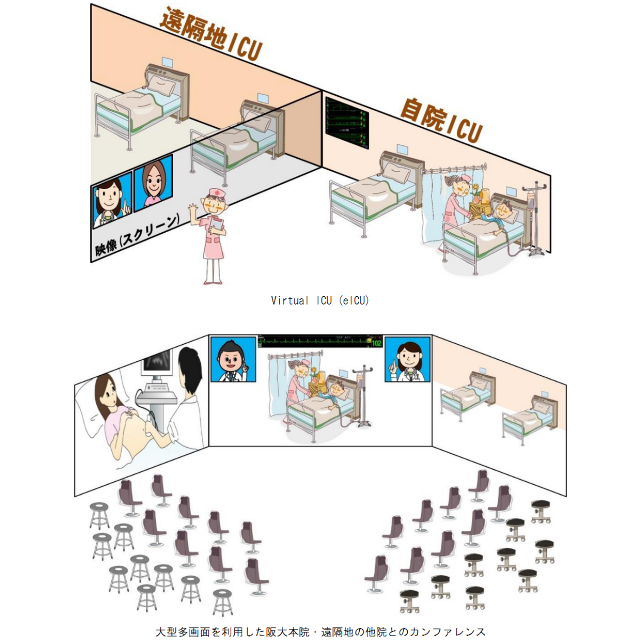
The meeting was between the Osaka University Clinical Trial Hospital, which has less than one hundred beds, and the private hospital, which has less than three hundred beds.
Kanden Hospital in the north, Sumitomo Hospital in the south, and Kitano Hospital a little further east are located, so it is not that there is not enough medical care.
At the time of this initiative, we were looking for ways to attract the nearby Sakurabashi Watanabe Hospital.
I imagined that Osaka University would perform high-level cardiovascular surgery, and that a private hospital downstairs would see the post-operative care care without seeing it at Osaka University Hospital.
As a result, Osaka University Hospital does not have a hospital bed and concentrates on surgery, and the private hospital downstairs accepts patients who need intensive medical care called after-stage care, so that they can experience difficult cases and have the opportunity to get a high medical fee.
I thought that it would be okay for Osaka University Hospital to be able to do so at Osaka University Hospital with a specialized distinction and separation.
If this is a clinical trial base, it may need to be a hospital, but if it is a facility that provides advanced medical care, I thought that it would be good for a barbed clinic.
If you think about mainly patients from overseas, you will not be subject to the restrictions on medical treatment fees, so you can operate flexibly. I thought that if that model was established, it would be possible to ask Chuikyo and others to deliberate.
Among the people involved in the realization of Nakanoshima Qross, there are those who presented this concept, so I think that it will have a little impact as a draft.
This article has a lot of delusions.
Inspired by the original draft of Nakanoshima, I thought that the successor of Itami Hospital in the city was good for a complex type hospital.
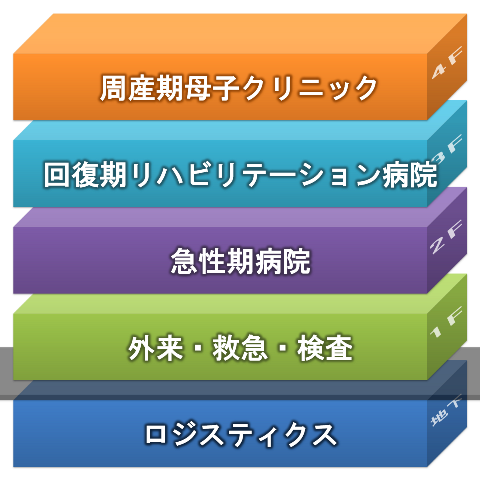
The first is an acute hospital consisting of a medical system centered on respirators and allergies, a surgical system centered on orthopedics, a circulatory and cardiovascular surgery that cooperates with cardiovascular medicine and cardiovascular surgery, and an acute hospital consisting of a digestive center where digestive medicine and digestive surgery cooperate.
The outpatient clinic is in charge of the general medical department, and the specialized outpatient clinic is connected to specialists in and outside the hospital.
Hospitalizations are limited to 30beds for advanced systems such as emergency, intensive care, and high care units, and 100-120beds for general hospitalizations in the acute phase.
The second is a barbed clinic specializing in perinatal mothers and children.
It depicts the image of the public and private sector. There are many unprofitable parts, but it is assumed that Itami City will be a sponsor as a measure to alleviate the decline of the regional population as much as possible.
If we can also manage the current Hanshin North Regional Children’s Emergency Center, I think it would be good to be able to respond seamlessly.
The third hospital is a rehabilitation hospital.
Patients admitted to the convalescent rehabilitation ward have a strict disease and duration.
Here mainly take the patient from the first orthopedic surgery. The first hospital does not have a rehabilitation room, and the third one will secure a rehabilitation facility and human resources on a scale that stands out in the Hanshin Medical Area.
| Disease | Maximum length of hospital stay |
|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular disease, spinal cord injury, head injury, shunt surgery for subarachnoid hemorrhage, brain tumor, encephalitis, myelitis, myelitis, multiple shrable sclerosis, ductile plexus injury, etc. | 150 days |
| Multiple-part trauma including severe cerebrovascular disorders, severe cervical spinal injuries and head injuries with higher-order brain dysfunction | 180 days |
| Fractures of the femoral, pelvis, spine, hip or knee joint, or after the onset of multiple fractures or more than the limbs, or postoperative conditions | 90 days |
| He has a discontinued syndrome due to rest at the time of surgery or treatment of pneumonia, etc., and the condition after surgery or after onset of the disease | 90 days |
| conditions after nerve, muscle or ligament damage in the femur, pelvis, spine, hip or knee joints | 60 days |
| Post-substituted for hip or knee joints | 90 days |
Itami City is also aware that there are concerns about shortages of convalescent rehabilitation beds. It is clearly stated in the documents.
If that is the case, it is thought that even if we open a rehabilitation hospital for a recovery phase, it will not put pressure on the private sector, and patients will not lose their place to go.
[Reference] Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: Outline of Reiwa’s Medical Remuneration Revision [Hospitalization III (Recovery Period)]
[Reference] Itami City Itami Hospital: Itami Hospital Management Enhancement Plan Reiwa5 (2023)June
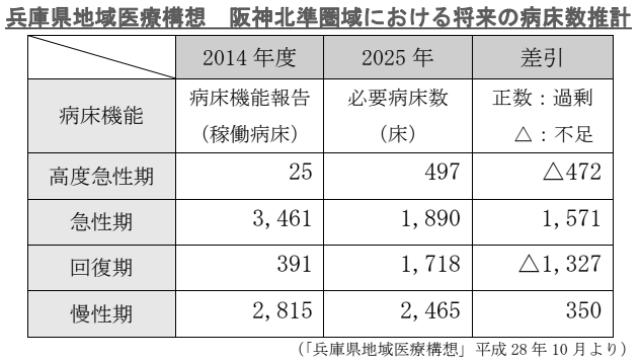
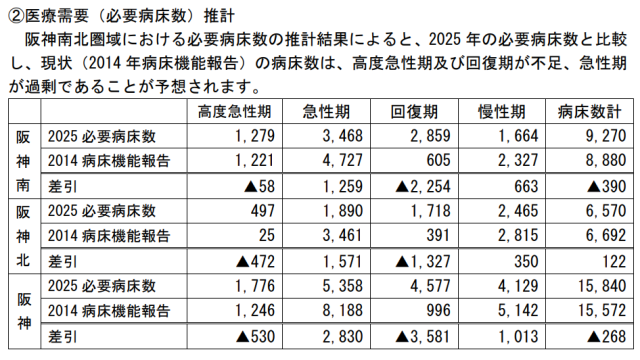
According to Itami City’s estimate, 472beds are insufficient in the acute phase, but in the acute phase, there are 1,571bed surpluses.
In the materials of Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital, the figures for both Hanshin Kita and Hanshin Minami are shown. Looking at this data, I suspect that there is something like impression manipulation in the materials of Itami City.
In the “Kita” of Hanshin, there was a shortage of 472beds in the highly acute phase, but in the Hanshin “South” there is a shortage of 58beds. In short, Hanshin Minami is in a state close to Plume Zero.
Even more remarkable is that until FY2016, Kansai Industrial Accident Hospital had thirty-six beds in the acute phase and sixty-two in the acute phase, but from FY2017, the number of minus 530beds in the Hanshin Medical Area has been converted to plus 82beds, since from FY2017, the number of minus 530beds in the Hanshin Medical Area has been reported in the 612th floor of the highly acute phase and zero floors in the acute phase.
In the Hanshin Medical Area, there are many highly acute hospital beds in Amagasaki and Nishinomiya, so it may be a good idea to use them.
In addition, in order to be able to convert acute care beds into highly acute stage beds, it may be necessary to have infrastructure that can discharge acute patients as quickly as possible.
This is where the recovery phase of the rehabilitation hospital comes in.

[Reference] Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital Public Medical Institutions, etc. 2025Plan
We will have patients with strokes and vulnerable fractures transferred to hospitals from the Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center and Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital as soon as possible.
Ultimately, the plan is to have the front hospital be transferred to the front hospital for one night and two days, and to be transferred to the (fantastic) resting rehabilitation hospital on the day after surgery.
I hope that the specialists of the front hospital will maximize the time to concentrate on the surgery, and that the postoperative care will be outsourced, and leave it to the (faginative) recovery rehabilitation hospital.
Even with my little experience, there were many patients in the ward of the neurosurgery ward that did not need to be seen by an expert doctor of neurosurgery. I needed an expert doctor to the point of surgery and post-operative observation, but on the third day I was calm, and in such a state, I was just waiting for the patient to recover, so I thought it would be better to have him take a break so that he can concentrate on the surgery so that he can concentrate on the surgery rather than calling the doctor to the ward with trivial things.
If this pattern is established, where doctors pick you up at the doctor car and transfer the hospital after the doctor takes over, it will be easier for you to make a profit, and it will be easier for you to fund the treatment of staff and the enhancement of facilities.

Number of beds (fantasy)
The new hospital is planned to have 602 floors, with 54 intensive care floors, 528 general hospital beds, and 20 palliative care beds.
In the case of the above-mentioned complex type hospital by function, I think that the first acute hospital should be about 20th to 30th intensive care and 100 to 120 general hospital beds.
The second perinatal mother-child clinic has a maximum of 19 floors.
Pregnant women are not sick, so I think it would be nice if you could spend a comfortable life in a whole private room on the top floor.
There are also infection control measures, so I think it would be nice to be able to respond around the clock by setting up an elevator dedicated to the mother-child clinic.
The third severancely rehabilitation hospital is expected to have less than two hundred beds, so I think that the convalescent ward will be operated on a maximum of 199th floor.
I think it would be good to have an ICU or HCU as needed. There is also a part that depends on how much it matches the needs of the region and cooperation with the first hospital.
If it is assigned as shown in the figure below, it will be a space that secures 200beds on one floor. However, in reality, construction costs are likely to be high unless you keep it to about a hundred floors, so I think that it will be vertically extended.
The perinatal mother-child clinic has nineteen floors, so there is too much space, but it is not bad that you can rehabilitate on the open top floor, so I think that half of it will be a rehabilitation room.
There are several cases of hospitals with one floor and one hundred floors, and four-story steel frames. Take, for example, the Sanuki Citizen Hospital. This is the site of 31,585m2, so it is about the same as the current Itami Hospital. The building area is 5,327m2, and it is 100th floor on one floor, so if you roughly double the size of 10,000m2, you can go to 200 floors per floor.
It is difficult to decide whether or not to establish a treatment bed in this complex type hospital.
Since the number of nursing care hospitals is increasing, it is thought that it will play a bridge between medical care and nursing care in the future.
Senri Chuo Hospital in Osaka is a hospital with four hundred beds directly connected to the station with a convalescent rehabilitation ward, a palliative care ward, and a general disabled ward. This hospital uses from the first basement floor to the sixth floor, but on top of it is a paid nursing home with nursing care operated by another corporation. It is a complex of hospitals and nursing care.
In terms of management, the owner of the building (the landlord), the hospital as a tenant, the nursing care facility, the dispensing pharmacy, the restaurant, etc. are each working on the same site.
At the time of the opening of this hospital, I think that there was no system called nursing care medical care hospital, but now the number of nursing care hospitals is increasing, so I thought that it would be good to consider the care mix hospital of the recovery rehabilitation hospital and the nursing care hospital.
I don’t know if it’s better to have something like a medical disability. As it is now, as a municipal hospital, it can do unprofitable projects as a public hospital, but if it is completely privatized, it is a business, so it is not possible to deal with unprofitable projects.
As for the medical facilities for children with disabilities, there are the Nishinomiya Sunago Medical and Welfare Center and Hyogo Central Hospital in Mita, so it is not a necessary situation, but I thought that there was room to consider.
[Reference] Sanuki Citizen Hospital
[Reference] Public Onomachi Regional Sogo Hospital
[Reference] Senri Central Hospital
The new hospital is planned with 602 floors, but I think borrowings can be reduced to a small amount by limiting it to less than 400 floors. If the scale is small, income will also decrease, but the risk may be reduced because the expenditure is also reduced.
It may be better to target a mid-level caremic hospital instead of a general hospital position, which is better suited to the medical needs of the area.
Specialized medical care depends on the clinic mall in front of the gate and other hospitals for about ten minutes by ambulance, so you may be able to live in the area.
If you have a large rotary that can be installed in three or four bus stops, you may be able to make it a bus terminal to various directions of the city. The difficulty is that the city hall is subtly far away, but I think that buses are one key to attracting customers from all over the city as a medical base.
I think it would be good to set up an entrance and exit on the 171st National Route so that you can get on and off several buses (wagons) at the same time. You can also use an ambulance or a doctor’s car.
In particular, ambulances have the advantage of entering the 171st National Route directly because they should be quick when entering the site.
The rental building is assumed to be a clinic mall, but I think that general shops can be included here.
Considering the lives of hospitalized patients, I think it would be good to have a beauty salon and an eyeglass shop, and considering the life after discharge, I think that real estate agents are also ant.
In terms of life support, it may be good to have something like a coin laundry or a cleaning shop.
I think that medical gyms (fitness) that have been increasing in recent years are easy to be caught well from the image of the place.
In the back of the clinic mall, I think it is possible to build a facility for the elderly if there is demand by leaving enough space to build another building.
I think it would be meaningful for the region if we could rationally organize hospital beds in the area and cooperate with each other so that each hospital can conduct sound management.
There is a method called “Regional Medical Cooperation Promotion Corporation” as a way to not compete, give in, and help each other.
A regional medical cooperation promotion corporation is not a kind of concept or concept, but an incorporated corporation that actually exists. We share medical functions in the region and cooperate with business. Not only medical institutions but also nursing care providers can participate.
In order to efficiently provide high-quality and appropriate medical care in the region, the Regional Medical Cooperation Promotion Corporation has established a policy (Policy for Promoting Medical Cooperation) to promote the cooperation of operations related to hospitals, etc. (medical cooperation promotion policy) in order to efficiently provide high-quality and appropriate medical care in the region, and is a system in which the prefectural governor of the prefectural governor approves (certification for promoting medical cooperation) to promote medical cooperation.
About the corporate system for promoting regional medical cooperation
In order to play a role in helping to achieve the regional medical care concept and the construction of a comprehensive community care system, we will perform the following tasks.
- Opening of hospitals, etc.
- Hospital beds between participating companies or within the same participating corporation
- Secure financial resources for each business item according to the medical cooperation promotion policy
- Personnel exchanges of doctors, nurses, etc. in accordance with labor laws and regulations
- Training to improve the quality of medical professionals
- Supply of pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, etc.
- When adjusting for pharmaceuticals and medical devices, the regional medical cooperation promotion corporation coordinates the bulk purchase, and the participating corporation, etc., for individual purchase agreements, the participating companies, etc., conclude.
- Lending the funds necessary for the work of participating hospitals, guaranteeing debts, and recruiting people who will take on the fund
The number of medical institutions in the Hanshin Medical Area is 1,814, of which there are 88 hospitals.
The total number of beds is 18,447, with 12,366 general hospital beds, 3,881 beds for sanatorium beds, and 2,154 beds for mental illness. It is difficult to put all hospital beds under the control of the regional cooperation promotion corporation, but it may be worthwhile just to start collaborating with a national public hospital alone.
The table below is a list of national and public hospitals in the Hanshin Medical Area and major hospital beds. It had 4,888 floors in total.
When calculating the number of beds per full-time doctor, the speciality is seen at Hyogo Central Hospital and the Self-Defense Forces Hanshin Hospital.
The Prefectural Amagasaki, Kansai Workers’ Accidents, and Prefectural Nishinomiya, which are responsible for the highly acute phase, are characterized by the small number of hospital beds carried by doctors.
| Medical institution name | Beds | Beds / full-time doctor | Full-time doctor | Part-time doctor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center | 730 | 1.77 | 412 | 157 |
| Japan Workers’ Health and Safety Organization | 642 | 3.10 | 207 | 363 |
| National Hospital Organization Hyogo Central Hospital | 460 | 17.31 | 26 | 18 |
| Kinki Central Hospital of the Public Schools Mutual Aid Association | 445 | 4.45 | 100 | 124 |
| Takarazuka City Hospital | 436 | 5.01 | 87 | 57 |
| Itami Hospital | 414 | 4.45 | 93 | 65 |
| Kawanishi City General Medical Center | 405 | 4.40 | 92 | 83 |
| Hyogo Prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital | 400 | 2.19 | 183 | 83 |
| Mita Municipal Hospital | 300 | 4.62 | 65 | 28. |
| Nishinomiya City Central Hospital | 257 | 5.71 | 45 | 94 |
| Hanshin Hospital | 200 | 8.00 | 22 | 22 |
| Ashiya City Hospital | 199 | 5.38 | 37 | 70 |
The two hospitals of Hyogo Central Hospital, which is not responsible for medical care only for the region, are not only responsible for medical care in the region, and Hyogo Central Hospital, which is responsible for special medical care as a national hospital such as neuromuscular diseases, are difficult to be familiar with the regional medical cooperation promotion corporation, and the number of hospital beds excluding the two hospitals is 4,206beds. It will be a hospital bed occupancy rate of 22.8% in the Hanshin Medical Area.
If a regional medical cooperation promotion corporation is established in a group of public hospitals, the current scale of 4206 floors will be secured.

The Regional Medical Cooperative Promotion Corporation will continue to provide the necessary medical care for the region by transferring human resources, hospital beds, and funds that serve as management resources.
It is also important for management to rationalize and discount the purchase price by jointly purchasing pharmaceuticals and medical treatment materials, but it is important to earn money in medical care, which is the sales of medical care.
Since children and perinatal periods are unprofitable, they can stop doing so, and if there is only so much that a full-time doctor can do, sharing the burden within the corporation can enhance the sustainability of pediatric medical care.
In the extreme, full-time pediatric doctors are concentrated in Amagasaki, and costs such as labor costs are borne by the Regional Medical Cooperative Promotion Corporation, which provides a foundation that does not lose all pediatric medical care, including emergency care, from the Hanshin Medical Area.
If this puts pressure on the medical work of local private hospitals, I think it would be good to have private hospitals responsible for pediatric medical care participate in the regional medical cooperation promotion corporation and create an environment where they can discuss the division of living in the area and the cost burden fairly.
Orthopedics and gastroenterological surgeries have a large number of patients, so I think that it is a medical care that you want to continue at any medical institution.
If you divide them into small pieces, you can concentrate on the surgery because of the difference in expertise.
By dividing it into two groups, a group that performs surgery using a bioclean operating room and special equipment, and a group that performs universal surgery that can be performed with universal equipment, it is possible to accelerate the collection time of heavy capital investment and increase the number of surges by increasing the number of surgeries and increasing sales. It is an important factor for management to reduce unnecessary waiting periods and increase the turnover rate of equipment and equipment.
Even without such a mechanism, organ transplants can be divided. I don’t think there are any hospitals in the city that have an organ transplant team, but I think there are hospitals that have transplant candidates and teams that care for patients after transplants.
If you want to have a heart transplant team, you have to always wait for two teams to get a donor’s heart and a heart transplant to the recipient.
If you get a report, the donor team will rush to the hospital where the donor is located with a cooler box, and you will have to arrange traffic when you return. If the arrangement of the charter plane is in cash, it is necessary to prepare millions of yen, and the take-off and landing time will be adjusted while watching the operation time of the donor.
It would be a reasonable cost to keep a stand for the opportunity to see if there are several such things, rather than the frequent ones.
Of course, doctors, nurses, and clinical engineering engineers involved in heart transplants are required to have advanced skills, and it is also required to maintain their highly skilled personnel.
By considering medical care with high rarity and unprofitability that someone has to bear, or it must be able to be treated somewhere, it will be easier to see the necessity of separation.
Medical care that can be profitable can also be subdivided and divided into subdivisions to increase rationality and expertise, increase profit margins, and ensure opportunities for doctors to study.

The surgical support robot da Vinci, which began to be used in Japan around the 2000s, has been introduced and has reduced its rarity even though it is not a large hospital after it was listed in the insurance list.
There are treatments and testing methods that do not apply to everyone, but there are treatments and methods for patients that should be applied.
If you know that a famous doctor of Chinese medicine is in the Sanin region, there are many patients who visit by plane, and there is a clinic where you can not get an appointment.
It is difficult to adopt personal services as a corporation, but if it is a rare device, there is a possibility of procurement.
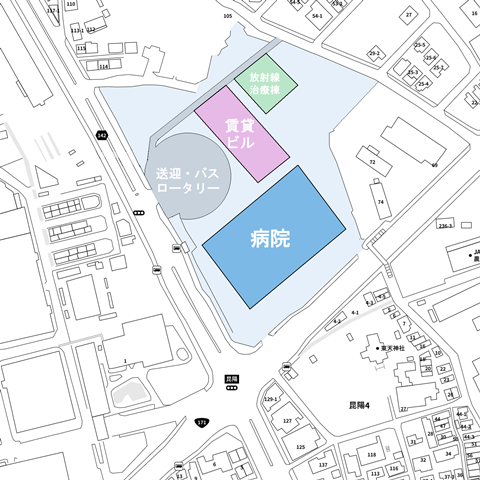
For example, special devices that are used for radiation therapy for cancer are highly rare. There are nineteen facilities in Japan for proton beams and six for heavy ionized rays.
The Osaka Heavy Ion ray center is located in front of Osaka Castle. I think that it is not aimed at Osaka Castle, but aims for a synergistic effect with the neighboring Osaka Prefectural Hospital Organization Osaka International Cancer Center.
“BNCT” (boronic neutron capture therapy) is a radiation therapy that has not yet become a major.
I don’t know if BNCT can be introduced in the location of Itami Hospital in the city, but it is thought that it is easy to obtain the cooperation of medical and engineering teachers of Osaka University.
I think that patients who have not been able to receive treatment anywhere in the country, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, will come to Itami from anywhere in the country when they expect BNCT with a desire to hold straw.
If you use Itami Airport well, you can arrive at the hospital by noon even from afar. If you can create such a pattern of making such a pattern, you can create an excursion demand for two nights and three days, and hotel demand, and hotel demand, which is the day after you stay at a hotel, after completing the preliminary inspection on the day of arrival.
The BNCT facility does not require inpatient facilities, so I think that using the hotel as well as medical examinations is sufficient.
[Reference] Medical Nuclear Technology Research Foundation Number of registered patients in each particle beam facility
[Reference] Osaka Medical and Pharmaceutical University: Kansai BNCT Joint Medical Center
See also: United Neutron: BNCT
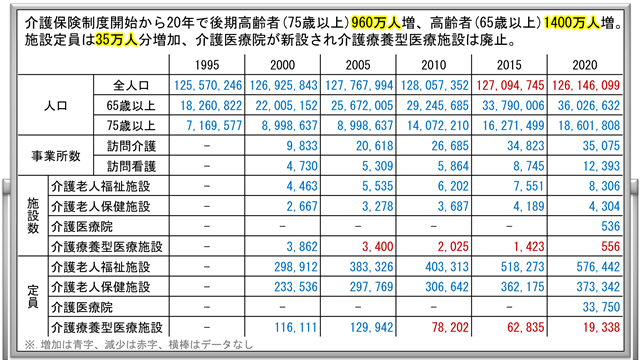
City 12Billion Yen + City Hospital 236Billion Yen
I have continued my own fantasy and delusions so far, but in reality, hospital construction is progressing.
The basic plan of the new hospital is being released in 2020 and 2023.
Since it changed dramatically in about three years, the size of the budget has changed. The material as of 2020 is worth 40.9 billion yen. It’s a heavy amount of money for a city of 20 million people.
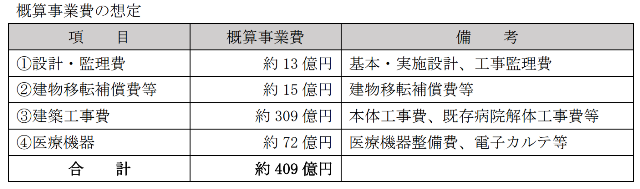
Three years later, it was changed to $562bn. The difference is the construction cost.

This is the first time I learned that the city burden is 12billion yen, and I think this is a tax. I think that the contribution of 12billion yen was decided by the city council, so it is consensus to be issued from taxes. Whether you like it or not, the citizens’ chosen city council members are taking it, so it is a matter of decision on 12billion yen.
Twenty-six billion yen is likely to be a challenge in the future.
The Itami Hospital is a public hospital in Itami City, because the owner of this municipal hospital is the mayor of Itami.
It is a debt because there was no deposit of 236billion yen at the time of the reconstruction decision, but because it is a debt because it is issued and borrowed.
As far as the explanation is concerned, the borrowed money can be repaid with the independent profit of the hospital, so it is said that the tax burden does not extend to citizens.
In the question, “If it is not possible to repay it, will it be out of the tax or will it be closed due to default?”, but it seems that the current situation is that it is not possible to answer the question “If it does not happen”, it seems that the current situation is that it is not possible to answer the question “If it does not happen”.
It seems that it will be returned in about thirty years, but I do not know if the base data that says it can be repaid is at the time of 40.9billion yen or whether it has been examined since it swelled to 562billion yen, but I think it is probably okay.
[Reference] Providing safe and secure medical care trusted by the community and creating health–We have started the construction of a new integrated hospital –
[Reference] Itami Hospital Management Enhancement Plan for the City of Itami Hospital Overview Version
[Reference] Basic Policy on the Integrated Reorganization of Itami Hospital and Kinki Central Hospital
This is my personal opinion on the blog.
If it is unprofitable in the public sector, it is a double suffering and triple suffering
According to the prefecture, the management status of Amagasaki Medical Center was severe, and in the fifth fiscal year of Reiwa, the company had a deficit of JPY1301 million in ordinary income and a loss of JPY1303 million in profit and loss of JPY1537 million in profit. The previous year was a surplus of about 1150million yen, so the drop is about 25 billion yen.
In the 5th fiscal year of Reiwa, the prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital also had a deficit of one billion and eighty-two million yen in ordinary income and eighty-seven million yen in profit and loss.
At two prefectural hospitals in the Hanshin Medical Area, there is a deficit of more than two billion yen in a single fiscal year. Other prefectural hospitals are also in the red, so it seems that the tax burden will be incurred in the form of a proposal for the entire prefecture as a whole.
2 The ordinary income of the hospital is as shown in the table below. The black-painted triangle mark indicates a minus (deficit).
| Year | Prefectural Amagasaki | Prefectural Nishinomiya |
|---|---|---|
| Reiwa 5th year | – 1315million yen | – 1 billion 28million yen |
| Reiwa 4th year | 114million yen | – 14400million yen |
| Reiwa 3rd year | 2913million yen | – 20million yen |
| Reiwa 2nd year | 2bn09million yen | – 315million yen |
| Reiwa first year | – 28million yen | – 88,000yen |
| Category: FY2018 | 30.5 million yen | 224million yen |
| FY2017 | 2345million yen | 320million yen |
Paying the deficit with prefectural taxes is a burden on the prefectural hospital that supports a wide area of medical care called the Hanshin Medical Area, so I think that as a citizen of the prefecture, I have no choice but to accept it.
On top of that, if you have to bear the deficit of the municipal hospital, the story will change.
If you divide two billion yen by the population of 175 million people in the Hanshin Medical Area, it is 1,143 yen per person. In fact, it is not only a burden for individuals because corporate taxes etc. are included.
I heard that the Itami Hospital of the city plans to return 236billion yen in thirty years, but if that is the case, it is about eighty billion yen a year. If the hospital balance is not surplused by eight billion yen, the hospital will not be able to pay back eight billion yen, and if the hospital does not keep a surplus of eight billion yen, it will default on its obligations.
If eighty million yen were to be shared by two hundred thousand citizens, it would be four thousand yen per person. Hospitals can be used not only by citizens but also outside the city and by foreigners, but the deficit compensation will be borne by the city residents and the company where they live.
[Reference] Hyogo Prefecture: Management status of Hyogo Prefecture Hospital Project in the 5th year of Reiwa
[Reference] Hyogo Prefecture: Management status of Hyogo Prefecture Hospital Project in the 3rd fiscal year of Reiwa
[Reference] Hyogo Prefecture: Management status of Hyogo Prefecture Hospital Project in the second year of Reiwa
[Reference] Hyogo Prefecture: FY2018 Hyogo Hospital Business Accounting Financial Results
Looking at the regular income of the prefectural hospital, it seems that there are good years and bad years.
In FY2017 and FY2018, we had a surplus of several hundred million yen, so I think that it was in line with the scale of the hospital bed size and medical demand so far.
In FY2019, in the fourth quarter, the new type of pneumonia (later the new coronavirus infection) began to spread, and the number of medical examinations progressed, so there were many medical institutions that were in the red.
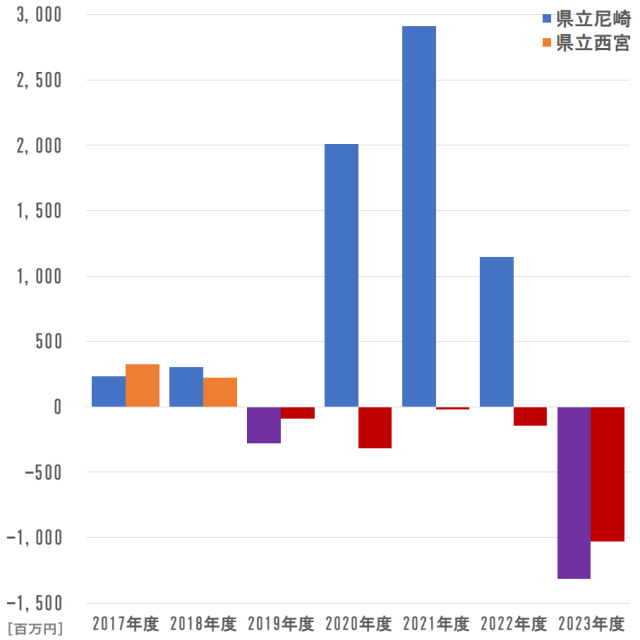
The Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki General Medical Center has a large hospital bed size, and the number of doctors is the same as that of a university hospital, so while there is potential to increase sales, the fixed cost is also large. If the hospital bed occupancy rate falls, it will record a large deficit.
The Prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital, Itami Hospital, and Kinki Chuo Hospital have nearly four hundred beds, but there is a difference of about twice the number of full-time doctors.
| Hospital name | Beds | Full-time doctor | Part-time doctor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyogo Medical University Hospital | 963 | 491 | 265 |
| Hyogo Prefectural Amagasaki Medical Center | 730 | 412 | 157 |
| Japan Workers’ Health and Safety Organization | 642 | 207 | 363 |
| Kinki Central Hospital of the Public Schools Mutual Aid Association | 445 | 100 | 124 |
| Takarazuka City Hospital | 436 | 87 | 57 |
| Itami Hospital | 414 | 93 | 65 |
| Hyogo Prefectural Nishinomiya Hospital | 400 | 183 | 83 |
| Nishinomiya City Central Hospital | 257 | 45 | 94 |
The new hospital is planned with 602beds, but if the full-time doctors of Itami Hospital and Kinki Chuo Hospital are taken over as it is, the number of beds is 200 people, the number of hospital beds close to Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital and the number of full-time doctors will be the number of full-time doctors.
At Kansai Workers’ Accident Hospital, you can see many professors at Osaka University, but it may be related to the number of part-time doctors 363.
It is a noteworthy project for medical managers, as there is a business plan that can fully repay eight billion yen a year with a 30-year loan of 236billion yen.
For citizens, there is an explanation that you can be relieved because it is in the black, so I think that there is a story that becomes a surplus somewhere.
In this day and age, if there is a management method that can continue to produce a surplus of eighty billion yen a year for thirty years, this is a better case to study together.
[Reference] City Itami Hospital: Outline of the hospital
[Reference] Itami Hospital Kinki Central Hospital Integration Committee materials, Itami Hospital management strengthening plan (draft)
[Reference] Minoh City Hospital: Business conditions
[Reference] Ikeda City Hospital:Hospital Indicators and Hospital Management
The aging of the population was self-evident, but due to the coronavirus pandemic, the number of births has decreased at a rapid pace, and the birthrate is progressing at an unexpected rate.
If the population continues to decline, the aging rate will naturally increase, but on the other hand, the elderly population will start to decline, so it is inevitable that the business of the elderly, where the majority of users such as medical care and nursing care are elderly, will inevitably lean toward shrinking.
According to the figures alone, the population of over-65s will peak in about fifteen years. Then, the population of over-75s peaks around 2055.
The application for nursing care facilities may be booming around 2040, when the baby boom junior generation becomes over 65years old, but after that, it seems that there are few new properties because it is assumed that there are more facilities. I think that it is a competition for vacant vacancies that result in the death of the baby boomer generation due to the death of the baby boomer generation, with the number of care refugees coming out one after another in the 2050s, when the baby-boom junior generation is over seventy-five years old.
The active-generation and working-age population that supports the elderly will not be able to maintain the current social security system, as it will not stop. In the 2000s, the population ratio was about four to one, but now it has been reduced to two to one, and by 2050 it will be less than one-and-a-half to one.
There is data that the medical expenses used by elderly people over the age of seventy-five are about nine million yen per person. In the social security system, which is burdened by the self-paying and the late-stage elderly care system, and the rest is borne by the working generation, it will afflict the lives of the working generation.
Since the working-age population of 15-64-year-olds will be up to about twice as much as the population over 75 years old by 2050, the income of the active generation may be collected for the late elderly, about 20,000yen per month.
In order to maintain medical care to a certain level, it is necessary to reduce the amount of medical care that is eligible for medical treatment fees or reduce the individual unit price.
There are also limits to lowering the unit price. Doctors and nurses have a strict process until obtaining a license, and the work is also hard, so there is no one who works at the minimum wage. Medical collapse will not be spared unless unit prices are maintained to a degree that does not worsen the treatment.
If the unit price does not go down, there is a way to get out of the insurance listing.
There is often a point where the problem of compresses is out of insurance.
For example, urinary incontinence surgery (K823: 235,100yen) and breast reconstruction (K022: 184,600yen) may be targeted. If this happens, cases may decrease due to urology, mammary surgery, plastic surgery, etc.
If the city hospital defaults on its debt because it can no longer keep up with its debt payments, creditors will be looking for someone else to pay them.
Public enterprise bonds are defined as follows
- It is a debt borne by local governments.
- It is a debt to be borne by financing.
- Have a form of deed borrowing or issuance of securities
- It is a debt with the tax rights of local governments as a real guarantee.
- The fulfillment of the debt is carried out beyond one fiscal year.
It appears that the corporate bonds borrowed by the Municipal Itami Hospital are, in other words, debts owed by the City of Itami. This is unconfirmed information, so please check with those in the know.
While we do not expect the hospital to default on its entire $23.6 billion debt with interest, there is a non-zero chance that if the hospital continues to lose money, it will not be able to repay the debt even once and will go bankrupt.
The revenue of the general account budget of Itami City for FY2025 is 92.7 billion yen, of which municipal tax is 34.3 billion yen. Expenditures are also 92.7 billion yen, including 67.8 billion yen for bonds, 100 million yen for reserve funds, and 4,000 yen for disaster recovery.
The ‘carryover’ within revenue is one thousand (1,000) yen. It is not 10,000 yen, but yen. It is only a budget.
According to the FY2023 financial data, the city’s debt (municipal bond balance) totaled 59,198,331,000 yen, including 24,874,267,000 yen in special bonds and 34,324,064,000 yen in general bonds, a decrease of 5,992,228,000 yen from the previous fiscal year.
Debt is down, which is a good thing.
A 6 billion yen reduction in debt per year means that that much money is being raised, but if 23.6 billion yen of debt is added to this amount, repayment will be a heavy burden.
One might think that to generate 800 million yen a year in new money from city expenditures, one would have to cut 1% of operations as a whole, but there are some items that cannot be easily cut, including personnel costs.
If spending cannot be cut, the only way is to increase revenues. Since we cannot pay off debt with debt and other sources of revenue are in jeopardy, it is likely that we will need to increase municipal tax revenue.
In an era of declining population, it may not be expected that resident tax revenue will increase due to population growth, but it may increase revenue due to an increase in citizen income.
[Reference] Ministry of Finance: Summary of the Local Government Bonds System
[Reference] Local Government Finance Organization
[Reference] Itami City: Outline of the initial budget (draft) in FY07 (FY2025) (including the February supplementary budget (draft) in FY2016)
[Reference] Itami City: Financial Results
Because it is a municipal hospital, the owner is the mayor, and the citizen is also a user and a logistical supporter.
I don’t think there is much awareness of users of the 64-year-old and younger, but I think the opportunities for receiving medical services will increase as they age.
It is decided that the hospital will be reopened to match the medical demand in Itami City, and it will be carried out based on the plan that great teachers and smart staff members have contemplating, so I think that citizens should keep quiet.
According to the explanation of the municipal hospital, it is said that citizens will not be in a situation to repay debts, so I think it is better to have such an expectation that funds that can be deposited in the city accounting will be generated by making a surplus.
In neighboring Takarazuka City, borrowing can be considerably reduced by donations from citizens, or a new hospital may be built without debt.
In neighboring Nishinomiya City, the municipal hospital has been abolished and the prefectural hospital will be reopened, so I think that the city will not benefit from the debt or pay off the debt after the consolidation and abolition.
We expect the new hospital to continue to be in the black.

This time, I was researching the medical situation in the Hanshin medical area where we are located, and I wrote a blog at the same time, I wrote an article about the result.
As for the data, there are still many parts that need to be dug deep, but I am not asked to analyze this area, so I will analyze it when my hands are free.
As the construction of the new hospital progressed, Takarazuka City Hospital, which was thought to be not so competitive, became increasingly likely to strengthen its functions by donation, and itami citizens also increased the possibility of flowing to Takarazuka. It’s a patient fight.
From such a place, I had to fantasize about downsizing and enriching the convalescent rehabilitation ward.
In conclusion, we had no choice but to take advantage of the new hospital concept, create a good hospital, and have a good hospital management.
I would like to pay attention to the future trends.

When viewing the database, a login screen may pop up as shown in the figure below. This is a measure to avoid excessive load caused by robot searches. We appreciate your cooperation.
Please enter “NES” as your user name to login.